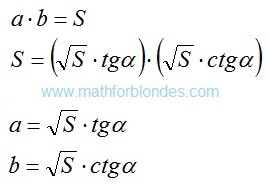Subject of occupations:
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS IN A RECTANGLE
Subject of the previous lesson
Division
Lesson 14
The linear angular functions
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS IN A RECTANGLE
Subject of the previous lesson
Division
Lesson 14
The linear angular functions
If to consider terminating trigonometric functions as coordinates of points of a unit circle in a Cartesian coordinate system, then the linear angular functions are coordinates of points of the chord connecting circle cross points to a coordinate. The sum of coordinates of any point of this chord is always equal to unit.
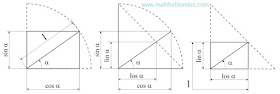 |
| The linear angular functions |
In mathematician of a concept, similar to the linear angular functions, are used since ancient times - it is division whole on a part. In the modern world an analog are percent.
The explanation for readers of this website. For myself I called the linear angular functions "linos" and "loses". How I thought up these names? Took designation of a sine and cosine. Visually they quite well differ. In each designation I replaced the first letter with the Latin letter "l" from the word "line". It turned out quite nicely. But to solve to you. Whether these functions in mathematician will get accustomed and as they will be called - time will show. I just offer one more mathematical tool for the description of reality.
At the following lesson we will consider
Addition
Addition