Equilateral triangle
 |
| Equilateral triangle |
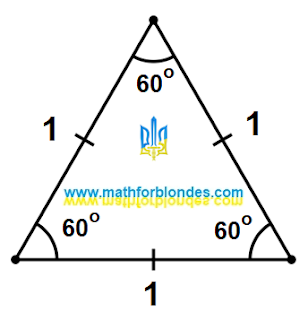
I have drawn an equilateral triangle with sides equal to one. I so want. The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. An equilateral triangle has three 60 degree angles. I don't know trigonometry yet.
Height of an equilateral triangle
 |
| Height of an equilateral triangle |
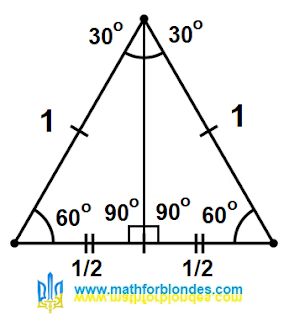
I drew the height in an equilateral triangle. The height is always perpendicular to the base of the triangle. If the height is drawn through the vertex of such a triangle, it will divide it into two equal right-angled triangles. This is always the case in isosceles triangles. An equilateral triangle is a special case of an isosceles triangle, in which the base is equal to the sides.
What happened as a result? The height divided the angle at the apex into two equal angles 60=30+30, it divided the base into two equal segments 1=(1/2)+(1/2). I still haven't heard anything about trigonometric functions.
Sine 30 degrees
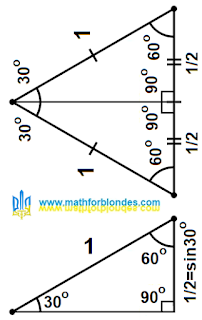
After that, someone came up with trigonometric functions. I was told that the sine of an angle in a right triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg to the hypotenuse. How do I find the sine value for a 30 degree angle? I just flip the picture 90 degrees and remove all unnecessary.
 |
| Sine 30 degrees |
The hypotenuse is equal to one. Any number divided by one does not change. So the length of the opposite leg in my triangle is equal to the sine of the angle of 30 degrees, that is, 1/2.
Cosine 30 degrees
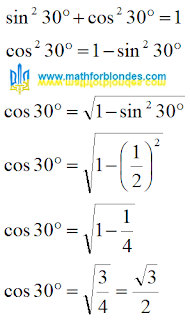
The cosine of 30 degrees I can easily find from the Pythagorean theorem. We take the Pythagorean theorem in our hands and count.
 |
| Cosine 30 degrees |
The cosine of 30 degrees turned out to be equal to the square root of three, divided by two.
Here's how easy it is to calculate. No tables needed.
No comments:
Post a Comment